Utilizing Visual Media to Improve Conceptual Understanding of Geometry Among Junior High School Students
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56855/jrsme.v4i2.1570Kata Kunci:
Visual Media, Conceptual Understanding, Geometry, Junior High SchoolAbstrak
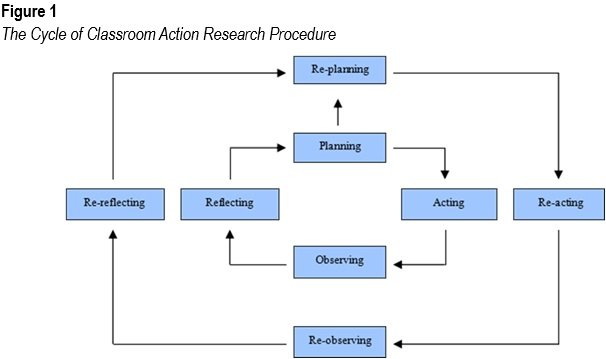
Purpose: This classroom action research aimed to improve junior high school students’ conceptual understanding of geometry through the integration of visual media within a cooperative learning framework. Methodology: The study was conducted in two cycles, involving 21 students, and followed the systematic stages of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. During the pre-cycle, traditional lecture-based instruction led to low engagement and unsatisfactory academic performance, with only 42.86% of students achieving the minimum mastery criterion (KKM). In Cycle I, the implementation of visual media such as diagrams and illustrations combined with cooperative learning activities, led to a modest increase in students’ average scores and engagement levels. However, the mastery rate remained at 52.38%, indicating the need for instructional refinement. In Cycle II, improvements in media quality, structured group facilitation, and enhanced teacher support contributed to significant learning gains. The average class score rose to 80.95, and 90.48% of students met the KKM. Observations also revealed marked improvements in student activeness, collaboration, and confidence in expressing ideas. Findings: The findings confirm that visual media, when effectively integrated into cooperative learning, significantly enhances students' conceptual understanding of geometry-related content. Significance: This research suggests that visual learning strategies should be systematically embedded into science instruction to support deeper comprehension and promote inclusive, student-centered classroom environments.
Referensi
Abrahamson, D., & Abdu, R. (2021). Towards an ecological-dynamics design framework for embodied-interaction conceptual learning: the case of dynamic mathematics environments. In Educational Technology Research and Development (Vol. 69, Issue 4). Springer US. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11423-020-09805-1
Amalia, L., Makmuri, M., & Hakim, L. El. (2024). Learning Design: To Improve Mathematical Problem-Solving Skills Using a Contextual Approach. JIIP - Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Pendidikan, 7(3), 2353–2366. https://doi.org/10.54371/jiip.v7i3.3455
Arsyad, M. (2016). The Efficiency Of Using Visual Learning Media In Improving The Understanding Of Science Concepts In Elementary School Students. Indonesian Journal Of Education (Injoe), 4(3), 1–23.
Ekmekci, A., & Serrano, D. M. (2022). The Impact of Teacher Quality on Student Motivation, Achievement, and Persistence in Science and Mathematics. Education Sciences, 12(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci12100649
Faradiba, S. S., Alifiani, & Md Nasir, N. A. (2024). the Resolution of Quadratic Inequality Problems in Mathematics: Discrepancies Between Thought and Action. Infinity Journal, 13(1), 61–82. https://doi.org/10.22460/infinity.v13i1.p61-82
Gök, T. (2023). Comparison of University Students ’ Graphic Interpretation Skills. Journal of Science Learning, 6(3), 339–346. https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v6i3.55419
González, A., Gallego-Sánchez, I., Gavilán-Izquierdo, J. M., & Puertas, M. L. (2025). Assessing Graph Theory Students’ Use and Formulation of Definitions through the Van Hiele Model. International Journal of Research in Undergraduate Mathematics Education, 0123456789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40753-024-00264-0
Gustina, D. M., & Mariana, N. (2025). Augmented Reality-Based Ethnomathematics Learning Media to Enhance Spatial Ability in 3D Geometry for Fifth Grade Elementary Students. JOURNAL OF INNOVATION AND RESEARCH IN PRIMARY EDUCATION, 4(2), 273–280.
Hsu, S. K., & Hsu, Y. (2024). Supporting Young Learners in Learning Geometric Area Concepts Through Static Versus Dynamic Representation and Imagination Strategies. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 23(2), 441–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-024-10481-3
Khotimah, H., & Hidayat, N. (2022). Interactive Digital Comic Teaching Materials to Increase Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes. International Journal of Elementary Education, 6(2), 245–258. https://dx.doi.org/10.23887/ijee.v6i2
Maqoqa, T. (2024). An Exploration of Learners’ Understanding of Euclidean Geometric Concepts: A Case Study of Secondary Schools in the OR Tambo Inland District of the Eastern Cape. E-Journal of Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences, 5(5), 658–675. https://doi.org/10.38159/ehass.2024557
Nasir, M., Cari, C., Sunarno, W., & Rahmawati, F. (2022). The effect of STEM-based guided inquiry on light concept understanding and scientific explanation. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(11). https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/12499
Naufal, M. A., Abdullah, A. H., Osman, S., Abu, M. S., Ihsan, H., & Rondiyah. (2021). Reviewing the Van Hiele model and the application of metacognition on geometric thinking. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 10(2), 597–605. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v10i2.21185
Novita, J., Budiman, C., & Ganap, N. N. (2025). The Effect of Verbal Plus Picture and Verbal only Information on Immediate Retention of Maritime Vocabulary. Cetta: Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan, 8, 101–111.
Panjaitan, M. B., Alamsyah, M., Siburian, M. F., Fatmawati, E., Uslan, U., & Siagian, G. (2023). Improving Students’ Learning Outcomes in Natural Science Subject for Third Grade of Elementary School Through Video Media. Jurnal Obsesi : Jurnal Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini, 7(3), 3253–3266. https://doi.org/10.31004/obsesi.v7i3.4632
Prameswari, B., & Haryani, F. (2023). Analysis of 8 Grader Students’ Performance At Smp Am in Understanding the Triangle Concept Based on Nctm Geometry Standard. MaPana:Jurnal Matematika Dan Pembelajaran, 11(2), 307–325. https://doi.org/10.24252/mapan.2023v11n2a7
Simamora, R. E., & Ramadhanta, S. A. (2024). Investigating the effects of Realistic Mathematics Education on mathematical creativity through a mixed-methods approach. Indonesian Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 7(2), 337. https://doi.org/10.24042/ijsme.v7i2.21221
Siswanto, D. H., Saputra, S. A., & Education, T. P. (2025). Deep Learning Approach To Teaching Multiplication Concepts Using Coin Media : Classroom Action Research In Elementary School. Jurnal Padamu Negeri, 2(2), 87–97.
Stahl, G. (2021). Redesigning mathematical curriculum for blended learning. Education Sciences, 11(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci11040165
Surbakti, R., & Umboh, S. E. (2024). Cognitive Load Theory : Implications for Instructional Design in Digital Classrooms. International Journal of Educational Narratives.
Susilana, R., Dewi, L., Rullyana, G., Hadiapurwa, A., & Khaerunnisa, N. (2022). Can microlearning strategy assist students’ online learning? Cakrawala Pendidikan, 41(2), 437–451. https://doi.org/10.21831/cp.v41i2.43387
Verawati, N. N. S. P., Rokhmat, J., Harjono, A., Makhrus, M., & Sukarso, A. S. (2025). Integrating Ethnoscience-PBL and Virtual Technology to Improve Critical Thinking Skills: A Literature Review and Model Design. TEM Journal, 14(2), 1878–1894. https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM142-84
Zhou, T., & Colomer, J. (2024). education sciences and Individual Accountability : A Systematic Review. Education Sciences.
Unduhan
Diterbitkan
Cara Mengutip
Terbitan
Bagian
Lisensi
Hak Cipta (c) 2025 Supratman supratman, Tundreng Syarifuddin

Artikel ini berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










