Conceptual Rigor of AI-Generated Mathematical Explanations: The Case of Vector Functions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56855/jrsme.v4i3.1862Kata Kunci:
Generative artificial intelligence, ChatGPT, Gemini, Vector functions, Mathematics education, Conceptual rigor, Qualitative analysisAbstrak
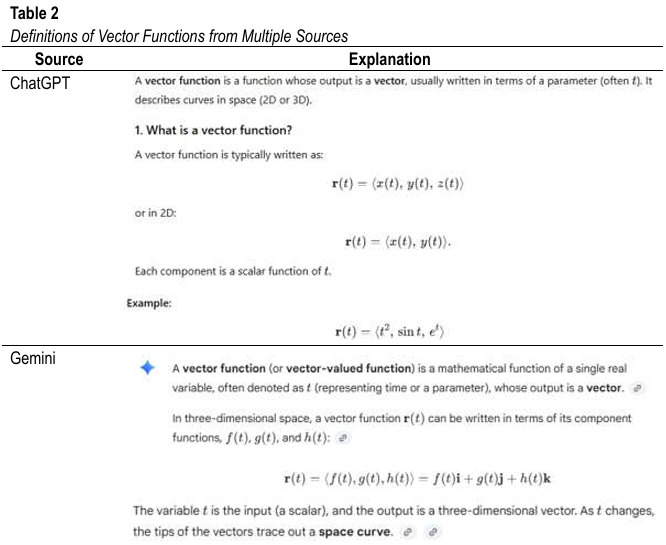
Purpose: The rapid rise of generative artificial intelligence has reshaped discussions in mathematics education, particularly regarding the capacity of advanced systems such as ChatGPT and Gemini to support conceptual rigor. This study aims to investigate how these generative AI tools define and explain vector functions, including the procedures for differentiating and integrating them, in order to evaluate their conceptual rigor of ai-generated mathematical explanations and pedagogical potential. Methodology: Employing a qualitative case study design, the research analyzed responses generated by ChatGPT and Gemini to a structured mathematical prompt on vector functions. The explanations were compared with authoritative calculus textbooks using qualitative content analysis and a standardized scoring rubric. Findings: Findings reveal that both systems provide broadly accurate introductory descriptions of vector functions, highlighting their component-wise structure. However, notable gaps emerge in mathematical precision, particularly in specifying domains, ranges, and the formal conditions underlying differentiability and integrability. ChatGPT tends to include intuitive geometric interpretations, whereas Gemini provides concise procedural explanations, yet both models lack the rigorous logical framing found in standard mathematical texts. Despite these limitations, the systems demonstrate consistent procedural accuracy in describing differentiation and integration of vector-valued functions. Significance: The results underscore the educational potential of generative AI while highlighting the need for teachers to critically evaluate AI-generated mathematical content, particularly when these tools are used to support students’ conceptual learning in mathematics. These findings also highlight important implications for AI literacy, instructional design, and future research in mathematics education.
Unduhan
Diterbitkan
Cara Mengutip
Terbitan
Bagian
Lisensi
Hak Cipta (c) 2025 Enny Listiawati, Hendra Kartika, Çiğdem Arslan

Artikel ini berlisensi Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.










